1 - A Tutorial Introduction (p. 5)
Let us begin with a quick introduction to C. Our aim is to show the essential elements of the language in real programs, but without getting bogged down in details, rules, and exceptions. At this point, we are not trying to be complete or even precise (save that the examples are meant to be correct). We want to get you as quickly as possible to the point where you can write useful programs, and to do that we have to concentrate on the basics: variables and constants, arithmetic, control flow, functions, and the rudiments of input and output. We are intentionally leaving out of this chapter features of C that are important for writing bigger programs. These include pointers, structures, most of C's rich set of operators, several control-flow statements, and the standard library.
This approach has its drawbacks. Most notable is that the complete story on any particular language feature is not found here, and the tutorial, by being brief, may also be misleading. And because the examples do not use the full power of C, they are not as concise and elegant as they might be. We have tried to minimize these effects, but be warned. Another drawback is that later chapters will necessarily repeat some of this chapter. We hope that the repetition will help you more than it annoys.
In any case, experienced programmers should be able to extrapolate from the material in this chapter to their own programming needs. Beginners should supplement it by writing small, similar programs of their own. Both groups can use it as a framework on which to hang the more detailed descriptions that begin in Chapter 2.
1.1 - Getting Started
The only way to learn a new programming language is by writing programs in it. The first program to write is the same for all languages (print the words):
hello, world
This is the big hurdle; to leap over it you have to be able to create the program text somewhere, compile it successfully, load it, run it, and find out where your output went. With these mechanical details mastered, everything else is comparatively easy.
In C, the program to print "hello, world" is
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
}
Just how to run this program depends on the system you are using. As a
specific example, on the UNIX operating system you must create the program in
a file whose name ends in .c, such as hello.c, then compile it with the
command
cc hello.c
If you haven't botched anything, such as omitting a character or misspelling
something, the compilation will proceed silently, and make an executable file
called a.out. If you run a.out by typing the command
a.out
it will print
hello, world
On other systems, the rules will be different; check with a local expert.
Variations and notes concerning the "hello, world" program in C
TLDR: It is now standard (literally part of the language standard) for main to have an explicit return type, namely int. If the terminating } for main is reached, then it's as if return 0; were included at the end of main, signifying that a successful exit status was emitted. Perhaps the clearest note on this matter may be found in [1], K&R C itself:
You may have noticed that there is a return statement at the end of
main. Sincemainis a function like any other, it may return a value to its caller, which is in effect the environment in which the program was executed. Typically, a return value of zero implies normal termination; non-zero values signal unusual or erroneous termination conditions. In the interests of simplicity, we have omittedreturnstatements from ourmainfunctions up to this point, but we will include them hereafter, as a reminder that programs should return status to their environment.
If you ran the hello.c program as it exists above, using cc hello.c, then you might get the following warning:
hello.c:3:1: warning: type specifier missing, defaults to 'int' [-Wimplicit-int]
main()
^
1 warning generated.
We could retry with cc -ansi hello.c, and the warning would go away, but it might be worth understanding why the warning was produced in the first place. We could follow the advice in this post by giving main a return type (i.e., int main()) and then use return 0; as the last statement in the definition of main() — the warning would go away, but, again, we wouldn't really be all that closer to understanding why we need int main() in the first place.
The explanation, it turns out, is primarily historical. This post, which lists places to find various C/C++ standard documents, can lead us to a key excerpt from ISO/IEC 9899:2018 (C17/C18) (p. 11):
If the return type of the
mainfunction is a type compatible withint, a return from the initial call to themainfunction is equivalent to calling theexitfunction with the value returned by themainfunction as its argument; reaching the}that terminates themainfunction returns a value of0. If the return type is not compatible withint, the termination status returned to the host environment is unspecified.
Of course, this excerpt concerns the main function specifically, which has special significance in C; in general, however, it is helpful to note the following excerpt from the same document (p. 114):
If the
}that terminates a function is reached, and the value of the function call is used by the caller, the behavior is undefined.
Consequently, as this post notes, the return statement is never mandatory at the end of a function, even if the function return type is not void. No diagnostic is required and it is not undefined behavior; for example, consider the following (defined behavior):
int foo(void)
{
}
int main()
{
foo();
}
Reading the return value of foo (lines 1-3 above) is undefined behavior per the second excerpt above:
int bla = foo(); // undefined behavior
But the main function is an exception to this rule — per the first excerpt, if the } terminating main is reached, then this is equivalent to there being a return 0; statement at the end of main.
Why does any of this matter? The answer has its roots in Unix (the birthplace of C), specifically the importance of exit status codes. The Wiki page has a useful excerpt as it pertains to C in particular:
The C programming language allows programs exiting or returning from the main function to signal success or failure by returning an integer, or returning the macros
EXIT_SUCCESSandEXIT_FAILURE. On Unix-like systems these are equal to0and1, respectively. A C program may also use theexit()function specifying the integer status or exit macro as the first parameter.The return value from
mainis passed to theexitfunction, which for values zero,EXIT_SUCCESSorEXIT_FAILUREmay translate it to "an implementation defined form" of successful termination or unsuccessful termination.Apart from zero and the macros
EXIT_SUCCESSandEXIT_FAILURE, the C standard does not define the meaning of return codes. Rules for the use of return codes vary on different platforms (see the platform-specific sections).
Some examples are provided below of successful and unsuccessful hello.c programs and the output of trying to compile and then execute the program and then run a subsequent "program", echo "Nice!", based on the successful compilation/termination of the hello.c program.
Examples
- Ex. 1
- Ex. 2
- Ex. 3
- Ex. 4
- Ex. 5 (fail)
- Ex. 6
- Ex. 7 (fail)
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
}
cc hello.c && ./a.out && echo "Nice!"
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
}
cc -ansi hello.c && ./a.out && echo "Nice!"
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
}
cc hello.c && ./a.out && echo "Nice!"
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
return 0;
}
cc hello.c && ./a.out && echo "Nice!"
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
return 8;
}
cc hello.c && ./a.out && echo "Nice!"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
cc hello.c && ./a.out && echo "Nice!"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
cc hello.c && ./a.out && echo "Nice!"
- Out 1
- Out 2
- Out 3
- Out 4
- Out 5
- Out 6
- Out 7
hello.c:3:1: warning: type specifier missing, defaults to 'int' [-Wimplicit-int]
main()
^
1 warning generated.
hello, world
Nice!
hello, world
Nice!
hello, world
Nice!
hello, world
Nice!
hello, world
hello, world
Nice!
hello, world
- Why 1
- Why 2
- Why 3
- Why 4
- Why 5
- Why 6
- Why 7
This is the original hello.c program along with the generated warning remarked on previously (due to the fact that main is not declared with an explicit int return type, as shown on line 3, the highlighted line).
We did not modify the original hello.c program, only the manner in which it was compiled. Specifically, cc hello.c && ./a.out && echo "Nice!" was changed to cc -ansi hello.c && ./a.out && echo "Nice!". The presence of the -ansi flag, or the equivalent -std=c89 flag, ensures we're running the compiler to respect constraints as defined when K&R C was written. Hence, there's no warning.
An explicit int return type has been added to main (line 3), and we have implicitly taken advantage of C's special treatment of main as defined in the C17 standard:
[...] reaching the
}that terminates themainfunction returns a value of0[...]
An explicit return statement, return 0;, was added to the end of main (line 6). Since 0 signals a successful termination, the output is Nice!, as expected.
Instead of relying on an implicit return in main or returning 0 (which signals success), we explicitly return a non-zero integer (line 6) — a non-zero integer return value indicates failure. Hence, cc hello.c compiles the program, we execute it with ./a.out, and hello, world prints as expected, but the termination of the program indicates failure; thus, echo "Nice!" does not run as a result.
We now make use of the <stdlib.h> header and the EXIT_SUCCESS macros contained therein (lines 2 and 7). The result is predictable.
We now make use of the <stdlib.h> header and the EXIT_FAILURE macros contained therein (lines 2 and 7). The result is predictable.
As noted in this answer, a lot of the discussion around the most appropriate choice of main(), int main(), int main(void), etc., is highly standard-version dependent; thus, a general answer would not be entirely accurate. As this answer notes, there's no difference between main() and main(void) in C under ordinary circumstances; under un-ordinary circumstances, however, if you write your own call to main, then main() will permit you to pass it any parameters you like, while main(void) will force you to pass it none. Still, none of this matters in terms of the 99.99999999% case, which is main being invoked by the runtime to launch your program. The runtime neither knows nor cares if you write main() or main(void); it is worth noting that if you code the standard int main(int argc, char **argv) you will get your command-line parameters in there.
Keith Thompson on Quora has a rather direct answer to why we should write int main() as opposed to void main() or just main(): because the language standard says so.
Why does it say so? Because many operating systems use the status returned by the
mainprogram, and because in C thevoidtype and keyword wasn't even introduced until the language had been in use for a number of years, and there was no particular reason to change it whenvoidwas introduced.C and C++ are two different languages.
In C,
maincan be defined as:int main(void) { /* … */ }or
int main(int argc, int *argv[]) { /* … */ }or equivalent, or in some other implementation-defined way. So a compiler can accept
void main(), but it's not required to — and there's no good reason not to use one of the standard forms.For C++, it's mostly the same — except that the parameterless form is
int main() { /* … */ }though C++ allows
(void)for compatibility with C. (Empty parentheses have a different meaning in C++ than in C). C++ also allows other implementation-defined forms — but the return type must beint.(All this is for hosted implementations. For freestanding implementations, typically for targets with no operating system, the program entry point is implementation-defined, and might not even be called
main.)
All of this to say: there's no silver bullet for an answer — most responses will have merit. Effective answers depend on the question (as usual).
A note about the a.out command
If you blindly try to execute the a.out program by typing the command a.out, then you will likely encounter some sort of Unknown command error.
As others on this thread have noted, this problem is more of a shell-related problem than a C problem. See the top answer for more details — the short version is that you should type the command ./a.out in the same directory as a.out (this tells the shell to look for a.out in the current directory).
Now for some explanations about the program itself:
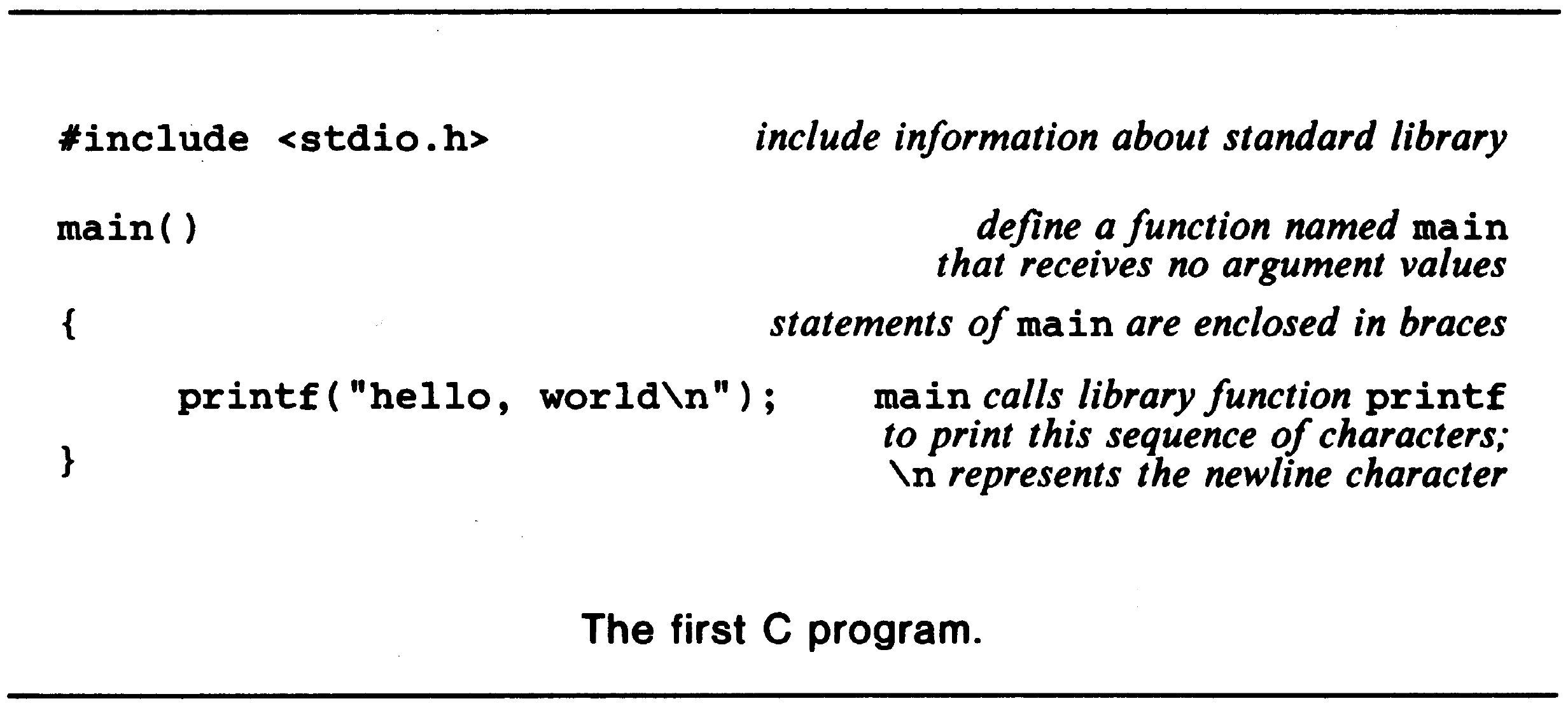
A C program, whatever
its size, consists of functions and variables. A function contains statements
that specify the computing operations to be done, and variables store
values used during the computation. C functions are like the subroutines and
functions of Fortran or the procedures and functions of Pascal. Our example is
a function named main. Normally you are at liberty to give functions whatever
names you like, but "main" is special — your program begins executing at the
beginning of main. This means that every program must have a main somewhere.
main will usually call other functions to help perform its job, some that you
wrote, and others from libraries that are provided for you. The first line of the
program,
#include <stdio.h>
tells the compiler to include information about the standard input/output library; this line appears at the beginning of many C source files. The standard library is described in Chapter 7 and Appendix B.
One method of communicating data between functions is for the calling
function to provide a list of values, called arguments, to the function it calls.
The parentheses after the function name surround the argument list. In this
example, main is defined to be a function that expects no arguments, which is
indicated by the empty list ( ).
The statements of a function are enclosed in braces { }. The function main
contains only one statement:
printf("hello, world\n");
A function is called by naming it, followed by a parenthesized list of arguments,
so this calls the function printf with the argument "hello, world\n".
printf is a library function that prints output, in this case the string of characters
between the quotes.
A sequence of characters in double quotes, like "hello, world\n", is
called a character string or string constant. For the moment our only use of
character strings will be as arguments for printf and other functions.
The sequence \n in the string is C notation for the newline character, which
when printed advances the output to the left margin on the next line. If you
leave out the \n (a worthwhile experiment), you will find that there is no line
advance after the output is printed. You must use \n to include a newline
character in the printf argument; if you try something like
printf("hello, world
");
the C compiler will produce an error message.
printf never supplies a newline automatically, so several calls may be used
to build up an output line in stages. Our first program could just as well have
been written
#include <stdio.h>
main()
{
printf("hello, ");
printf("world");
printf("\n");
}
to produce identical output.
Notice that \n represents only a single character. An escape sequence like
\n provides a general and extensible mechanism for representing hard-to-type
or invisible characters. Among the others that C provides are \t for tab, \b
for backspace, \" for the double quote, and \\ for the backslash itself. There
is a complete list in Section 2.3.
Exercises
1.2 - Variables and Arithmetic Expressions
The next program uses the formula to print the following table of Fahrenheit temperatures and their centigrade or Celsius equivalents:
0 -17
20 -6
40 4
60 15
80 26
100 37
120 48
140 60
160 71
180 82
200 93
220 104
240 115
260 126
280 137
300 148
The program itself still consists of the definition of a single function named
main. It is longer than the one that printed "hello, world", but not complicated.
It introduces several new ideas, including comments, declarations, variables,
arithmetic expressions, loops, and formatted output.
#include <stdio.h>
/* print Fahrenheit-Celsius table
for fahr = 0, 20, ..., 300 */
main()
{
int fahr, celsius;
int lower, upper, step;
lower = 0; /* lower limit of temperature table */
upper = 300; /* upper limit */
step = 20; /* step size */
fahr = lower;
while (fahr <= upper) {
celsius = 5 * (fahr - 32) / 9;
printf("%d\t%d\n", fahr, celsius);
fahr = fahr + step;
}
}
The two lines
/* print Fahrenheit-Celsius table
for fahr = 0, 20, ..., 300 */
are a comment, which in this case explains briefly what the program does. Any
characters between /* and */ are ignored by the compiler; they may be used
freely to make a program easier to understand. Comments may appear anywhere
a blank or tab or newline can.
In C, all variables must be declared before they are used, usually at the beginning of the function before any executable statements. A declaration announces the properties of variables; it consists of a type name and a list of variables, such as
int fahr, celsius;
int lower, upper, step;
The type int means that the variables listed are integers, by contrast with
float, which means floating point, i.e., numbers that may have a fractional
part. The range of both int and float depends on the machine you are
using; 16-bit ints, which lie between and , are common, as are
32-bit ints. A float number is typically a 32-bit quantity, with at least six
significant digits and magnitude generally between about and .
C provides several other basic data types besides int and float, including:
char character - a single byte
short short integer
long long integer
double double-precision floating point
The sizes of these objects are also machine-dependent. There are also arrays, structures and unions of these basic types, pointers to them, and functions that return them, all of which we will meet in due course.
Computation in the temperature conversion program begins with the assignment statements
lower = 0;
upper = 300;
step = 20;
fahr = lower;
which set the variables to their initial values. Individual statements are terminated by semicolons.
Each line of the table is computed the same way, so we use a loop that
repeats once per output line; this is the purpose of the while loop
while (fahr <= upper) {
...
}
The while loop operates as follows: The condition in parentheses is tested. If
it is true (fahr is less than or equal to upper), the body of the loop (the three
statements enclosed in braces) is executed. Then the condition is re-tested, and
if true, the body is executed again. When the test becomes false (fahr exceeds
upper) the loop ends, and execution continues at the statement that follows the
loop. There are no further statements in this program, so it terminates.
The body of a while can be one or more statements enclosed in braces, as
in the temperature converter, or a single statement without braces, as in
while (i < j)
i = 2 * i;
In either case, we will always indent the statements controlled by the while by
one tab stop (which we have shown as four spaces) so you can see at a glance
which statements are inside the loop. The indentation emphasizes the logical
structure of the program. Although C compilers do not care about how a program
looks, proper indentation and spacing are critical in making programs easy
for people to read. We recommend writing only one statement per line, and
using blanks around operators to clarify grouping. The position of braces is less
important, although people hold passionate beliefs. We have chosen one of
several popular styles. Pick a style that suits you, then use it consistently.
Most of the work gets done in the body of the loop. The Celsius temperature
is computed and assigned to the variable celsius by the statement
celsius = 5 * (fahr - 32) / 9;
The reason for multiplying by 5 and then dividing by 9 instead of just multiplying
by 5/9 is that in C, as in many other languages, integer division truncates:
any fractional part is discarded. Since 5 and 9 are integers, 5/9 would be
truncated to zero and so all the Celsius temperatures would be reported as zero.
This example also shows a bit more of how printf works. printf is a
general-purpose output formatting function, which we will describe in detail in
Chapter 7. Its first argument is a string of characters to be printed, with each
% indicating where one of the other (second, third, ... ) arguments is to be substituted,
and in what form it is to be printed. For instance, %d specifies an integer
argument, so the statement
printf("%d\t%d\n", fahr, celsius);
causes the values of the two integers fahr and celsius to be printed, with a
tab (\t) between them.
Each % construction in the first argument of printf is paired with the
corresponding second argument, third argument, etc.; they must match up properly
by number and type, or you'll get wrong answers.
By the way, printf is not part of the C language; there is no input or output
defined in C itself. printf is just a useful function from the standard
library of functions that are normally accessible to C programs. The behavior
of printf is defined in the ANSI standard, however, so its properties should be
the same with any compiler and library that conforms to the standard.
In order to concentrate on C itself, we won't talk much about input and output
until Chapter 7. In particular, we will defer formatted input until then. If
you have to input numbers, read the discussion of the function scanf in Section
7.4. scanf is like printf, except that it reads input instead of writing
output.
There are a couple of problems with the temperature conversion program.
The simpler one is that the output isn't very pretty because the numbers are not
right-justified. That's easy to fix; if we augment each %d in the printf statement
with a width, the numbers printed will be right-justified in their fields.
For instance, we might say
printf("%3d %6d\n", fahr, celsius);
to print the first number of each line in a field three digits wide, and the second in a field six digits wide, like this:
0 -17
20 -6
40 4
60 15
80 26
100 37
...
The more serious problem is that because we have used integer arithmetic, the Celsius temperatures are not very accurate; for instance, is actually about , not . To get more accurate answers, we should use floating-point arithmetic instead of integer. This requires some changes in the program. Here is a second version:
#include <stdio.h>
/* print Fahrenheit-Celsius table
for fahr = 0, 20, ..., 300; floating-point version */
main()
{
float fahr, celsius;
int lower, upper, step;
lower = 0; /* lower limit of temperature table */
upper = 300; /* upper limit */
step = 20; /* step size */
fahr = lower;
while (fahr <= upper) {
celsius = (5.0 / 9.0) * (fahr - 32);
printf("%3.0f %6.1f\n", fahr, celsius);
fahr = fahr + step;
}
}
This is much the same as before, except that fahr and celsius are
declared to be float, and the formula for conversion is written in a more
natural way. We were unable to use 5/9 in the previous version because
integer division would truncate it to zero. A decimal point in a constant indicates
that it is floating point, however, so 5.0/9.0 is not truncated because it
is the ratio of two floating-point values.
If an arithmetic operator has integer operands, an integer operation is performed.
If an arithmetic operator has one floating-point operand and one
integer operand, however, the integer will be converted to floating point before
the operation is done. If we had written fahr - 32, the 32 would be automatically
converted to floating point. Nevertheless, writing floating-point constants
with explicit decimal points even when they have integral values emphasizes
their floating-point nature for human readers.
The detailed rules for when integers are converted to floating point are in Chapter 2. For now, notice that the assignment
fahr = lower;
and the test
while (fahr <= upper)
also work in the natural way — the int is converted to float before the operation
is done.
The printf conversion specification %3.0f says that a floating-point
number (here fahr) is to be printed at least three characters wide, with no
decimal point and no fraction digits. %6.1f describes another number
(celsius) that is to be printed at least six characters wide, with 1 digit after
the decimal point. The output looks like this:
0 -17.8
20 -6.7
40 4.4
...
Width and precision may be omitted from a specification: %6f says that the
number is to be at least six characters wide; %.2f specifies two characters after
the decimal point, but the width is not constrained; and %f merely says to print
the number as floating point.
%d print as decimal integer
%6d print as decimal integer, at least 6 characters wide
%f print as floating point
%6f print as floating point, at least 6 characters wide
%.2f print as floating point, 2 characters after decimal point
%6.2f print as floating point, at least 6 wide and 2 after decimal point
Among others, printf also recognizes %o for octal, %x for hexadecimal, %c for
character, %s for character string, and %% for % itself.
Exercises
1.3 - The For Statement
There are plenty of different ways to write a program for a particular task. Let's try a variation on the temperature converter.
#include <stdio.h>
/* print Fahrenheit-Celsius table */
main()
{
int fahr;
for (fahr = 0; fahr <= 300; fahr = fahr + 20)
printf("%3d %6.1f\n", fahr, (5.0/9.0) * (fahr - 32));
}
This produces the same answers, but it certainly looks different. One major
change is the elimination of most of the variables; only fahr remains, and we
have made it an int. The lower and upper limits and the step size appear only
as constants in the for statement, itself a new construction, and the expression
that computes the Celsius temperature now appears as the third argument of
printf instead of as a separate assignment statement.
This last change is an instance of a general rule — in any context where it is
permissible to use the value of a variable of some type, you can use a more complicated
expression of that type. Since the third argument of printf must be
a floating-point value to match the %6.1f, any floating-point expression can
occur there.
The for statement is a loop, a generalization of the while. If you compare
it to the earlier while, its operation should be clear. Within the parentheses,
there are three parts, separated by semicolons. The first part, the initialization
fahr = 0
is done once, before the loop proper is entered. The second part is the test or condition that controls the loop:
fahr <= 300
This condition is evaluated; if it is true, the body of the loop (here a single
printf) is executed. Then the increment step
fahr = fahr + 20
is executed, and the condition re-evaluated. The loop terminates if the condition
has become false. As with the while, the body of the loop can be a single
statement, or a group of statements enclosed in braces. The initialization, condition,
and increment can be any expressions.
The choice between while and for is arbitrary, based on which seems
clearer. The for is usually appropriate for loops in which the initialization aud
increment are single statements and logically related, since it is more compact
than while and it keeps the loop control statements together in one place.
Exercises
1.4 - Symbolic Constants
A final observation before we leave temperature conversion forever. It's bad
practice to bury "magic numbers" like 300 and 20 in a program; they convey
little information to someone who might have to read the program later, and
they are hard to change In a systematic way. One way to deal with magic
numbers is to give them meaningful names. A #define line defines a symbolic
name or symbolic constant to be a particular string of characters:
#define <name replacement text>
Thereafter, any occurrence of name (not in quotes and not part of another name) will be replaced by the corresponding replacement text. The name has the same form as a variable name: a sequence of letters and digits that begins with a letter. The replacement text can be any sequence of characters; it is not limited to numbers.
#include <stdio.h>
#define LOWER 0 /* lower limit of table */
#define UPPER 300 /* upper limit */
#define STEP 20 /* step size */
/* print Fahrenheit-Celsius table */
main()
{
int fahr;
for (fahr = LOWER; fahr <= UPPER; fahr = fahr + STEP)
printf("%3d %6.1f\n", fahr, (5.0 / 9.0) * (fahr - 32));
}
The quantities LOWER, UPPER and STEP are symbolic constants, not variables,
so they do not appear in declarations. Symbolic constant names are conventionally
written in upper case so they can be readily distinguished from lower case
variable names. Notice that there is no semicolon at the end of a #define
line.
1.5 - Character Input and Output
We are now going to consider a family of related programs for processing character data. You will find that many programs are just expanded versions of the prototypes that we discuss here.
The model of input and output supported by the standard library is very simple. Text input or output, regardless of where it originates or where it goes to, is dealt with as streams of characters. A text stream is a sequence of characters divided into lines; each line consists of zero or more characters followed by a newline character. It is the responsibility of the library to make each input or output stream conform to this model; the C programmer using the library need not worry about how lines are represented outside the program.
The standard library provides several functions for reading or writing one
character at a time, of which getchar and putchar are the simplest. Each
time it is called, getchar reads the next input character from a text stream
and returns that as its value. That is, after
c = getchar()
the variable c contains the next character of input. The characters normally
come from the keyboard; input from files is discussed in Chapter 7.
The function putchar prints a character each time it is called:
putchar(c)
prints the contents of the integer variable c as a character, usually on the
screen. Calls to putchar and printf may be interleaved; the output will
appear in the order in which the calls are made.
1.5.1 - File Copying
Given getchar and putchar, you can write a surprising amount of useful
code without knowing anything more about input and output. The simplest
example is a program that copies its input to its output one character at a time:
<read a character>
while (<character is not end-of-file indicator>)
<output the character just read>
<read a character>
Converting this into C gives
#include <stdio.h>
/* copy input to output; 1st version */
main()
{
int c;
c = getchar();
while (c != EOF) {
putchar(c);
c = getchar();
}
}
The relational operator != means "not equal to."
What appears to be a character on the keyboard or screen is of course, like
everything else, stored internally just as a bit pattern. The type char is specifically
meant for storing such character data, but any integer type can be used.
We used int for a subtle but important reason.
The problem is distinguishing the end of the input from valid data. The
solution is that getchar returns a distinctive value when there is no more
input, a value that cannot be confused with any real character. This value is
called EOF, for "end of file." We must declare c to be a type big enough to
hold any value that getchar returns. We can't use char since c must be big
enough to hold EOF in addition to any possible char. Therefore we use int.
EOF is an integer defined in <stdio.h>, but the specific numeric value
doesn't matter as long as it is not the same as any char value. By using the
symbolic constant, we are assured that nothing in the program depends on the
specific numeric value.
The program for copying would be written more concisely by experienced C programmers. In C, any assignment, such as
c = getchar()
is an expression and has a value, which is the value of the left hand side after
the assignment. This means that an assignment can appear as part of a larger
expression. If the assignment of a character to c is put inside the test part of a
while loop, the copy program can be written this way:
#include <stdio.h>
/* copy input to output; 2nd version */
main()
{
int c;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF)
putchar(c);
}
The while gets a character, assigns it to c, and then tests whether the character
was the end-of-file signal. If it was not, the body of the while is executed,
printing the character. The while then repeats. When the end of the input is
finally reached, the while terminates and so does main.
This version centralizes the input — there is now only one reference to
getchar — and shrinks the program. The resulting program is more compact,
and, once the idiom is mastered, easier to read. You'll see this style often. (It's
possible to get carried away and create impenetrable code, however, a tendency
that we will try to curb.)
The parentheses around the assignment within the condition are necessary.
The precedence of != is higher than that of =, which means that in the absence
of parentheses the relational test != would be done before the assignment =. So
the statement
c = getchar() != EOF
is equivalent to
c = (getchar() != EOF)
This has the undesired effect of setting c to 0 or 1, depending on whether or not
the call of getchar encountered end of file. (More on this in Chapter 2.)
Exercises
1.5.2 - Character Counting
The next program counts characters; it is similar to the copy program.
#include <stdio.h>
/* count characters in input; 1st version */
main()
{
long nc;
nc = 0;
while (getchar() != EOF)
++nc;
printf("%ld\n", nc);
}
The statement
++nc;
presents a new operator, ++, which means increment by one. You could instead
write nc = nc + 1 but ++nc is more concise and often more efficient. There is a
corresponding operator -- to decrement by 1. The operators ++ and -- can be
either prefix operators (++nc) or postfix (nc++); these two forms have different
values in expressions, as will be shown in Chapter 2, but ++nc and nc++
both increment nc. For the moment we will stick to the prefix form.
The character counting program accumulates its count in a long variable
instead of an int. long integers are at least 32 bits. Although on some
machines, int and long are the same size, on others an int is 16 bits, with a
maximum value of 32767, and it would take relatively little input to overflow an
int counter. The conversion specification %ld tells printf that the
corresponding argument is a long integer.
It may be possible to cope with even bigger numbers by using a double
(double precision float). We will also use a for statement instead of a
while, to illustrate another way to write the loop.
#include <stdio.h>
/* count characters in input; 2nd version */
main()
{
double nc;
for (nc = 0; getchar() != EOF; ++nc)
;
printf("%.0f\n", nc);
}
printf uses %f for both float and double; %.0f suppresses printing of the
decimal point and the fraction part, which is zero.
The body of this for loop is empty, because all of the work is done in the
test and increment parts. But the grammatical rules of C require that a for
statement have a body. The isolated semicolon, called a null statement, is there
to satisfy that requirement. We put it on a separate line to make it visible.
Before we leave the character counting program, observe that if the input
contains no characters, the while or for test fails on the very first call to
getchar, and the program produces zero, the right answer. This is important.
One of the nice things about while and for is that they test at the top of the
loop, before proceeding with the body. If there is nothing to do, nothing is done,
even if that means never going through the loop body. Programs should act
intelligently when given zero-length input. The while and for statements
help ensure that programs do reasonable things with boundary conditions.
1.5.3 - Line Counting
The next program counts input lines. As we mentioned above, the standard library ensures that an input text stream appears as a sequence of lines, each terminated by a newline. Hence, counting lines is just counting newlines:
#include <stdio.h>
/* count lines in input */
main()
{
int c, nl;
nl = 0;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF)
if (c == '\n')
++nl;
printf("%d\n", nl);
}
The body of the while now consists of an if, which in turn controls the
increment ++nl. The if statement tests the parenthesized condition, and if the
condition is true, executes the statement (or group of statements in braces) that
follows. We have again indented to show what is controlled by what.
The double equals sign == is the C notation for "is equal to" (like Pascal's
single = or Fortran's .EQ.). This symbol is used to distinguish the equality test
from the single = that C uses for assignment. A word of caution: newcomers to
C occasionally write = when they mean ==. As we will see in Chapter 2, the
result is usually a legal expression, so you will get no warning.
A character written between single quotes represents an integer value equal
to the numerical value of the character in the machine's character set. This is
called a character constant, although it is just another way to write a small
integer. So, for example, 'A' is a character constant; in the ASCII character
set its value is 65, the internal representation of the character A. Of course 'A'
is to be preferred over 65: its meaning is obvious, and it is independent of a particular
character set.
The escape sequences used in string constants are also legal in character
constants, so '\n' stands for the value of the newline character, which is 10 in
ASCII. You should note carefully that '\n' is a single character, and in
expressions is just an integer; on the other hand, "\n" is a string constant that
happens to contain only one character. The topic of strings versus characters is
discussed further in Chapter 2.
Exercises
Write a program to count blanks, tabs, and newlines. [1]
Write a program to copy its input to its output, replacing each string of one or more blanks by a single blank. [1]
Write a program to copy its input to its output, replacing each tab by
\t, each backspace by\b, and each backslash by\\. This makes tabs and backspaces visible in an unambiguous way. [1]
1.5.4 - Word Counting
The fourth in our series of useful programs counts lines, words, and characters,
with the loose definition that a word is any sequence of characters that
does not contain a blank, tab or newline. This is a bare-bones version of the
UNIX program wc.
#include <stdio.h>
#define IN 1 /* inside a word */
#define OUT 0 /* outside a word */
/* count lines, words, and characters in input */
main()
{
int c, nl, nw, nc, state;
state = OUT;
nl = nw = nc = 0;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF) {
++nc;
if (c == '\n')
++nl;
if (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\t')
state = OUT;
else if (state == OUT) {
state = IN;
++nw;
}
}
printf("%d %d %d\n", nl, nw, nc);
}
Every time the program encounters the first character of a word, it counts
one more word. The variable state records whether the program is currently
in a word or not; initially it is "not in a word," which is assigned the value OUT.
We prefer the symbolic constants IN and OUT to the literal values 1 and 0
because they make the program more readable. In a program as tiny as this, it
makes little difference, but in larger programs, the increase in clarity is well
worth the modest extra effort to write it this way from the beginning. You'll
also find that it's easier to make extensive changes in programs where magic
numbers appear only as symbolic constants.
The line
nl = nw = nc = 0;
sets all three variables to zero. This is not a special case, but a consequence of the fact that an assignment is an expression with a value and assignments associate from right to left. It's as if we had written
nl = (nw = (nc = 0));
The operator || means OR, so the line
if (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\t')
says "if c is a blank or c is a newline or c is a tab". (Recall that the escape
sequence \t is a visible representation of the tab character.) There is a
corresponding operator && for AND; its precedence is just higher than ||.
Expressions connected by && or || are evaluated left to right, and it is
guaranteed that evaluation will stop as soon as the truth or falsehood is known.
If c is a blank, there is no need to test whether it is a newline or tab, so these
tests are not made. This isn't particularly important here, but is significant in
more complicated situations, as we will soon see.
The example also shows an else, which specifies an alternative action if the
condition part of an if statement is false. The general form is
if (<expression>)
<statement_1>
else
<statement_2>
One and only one of the two statements associated with an if-else is performed.
If the expression is true, statement_1 is executed; if not, statement_2 is
executed. Each statement can be a single statement or several in braces. In the
word count program, the one after the else is an if that controls two statements
in braces.
Exercises
1.6 - Arrays
Let us write a program to count the number of occurrences of each digit, of white space characters (blank, tab, newline), and of all other characters. This is artificial, but it permits us to illustrate several aspects of C in one program.
There are twelve categories of input, so it is convenient to use an array to hold the number of occurrences of each digit, rather than ten individual variables. Here is one version of the program:
#include <stdio.h>
/* counts digits, white space, others */
main()
{
int c, i, nwhite, nother;
int ndigit[10];
nwhite = nother = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
ndigit[i] = 0;
while ((c = getchar()) != EOF)
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
++ndigit[c-'0'];
else if (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\t')
++nwhite;
else
++nother;
printf("digits =");
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
printf(" %d", ndigit[i]);
printf(", white space = %d, other = %d\n",
nwhite, nother);
}
The output of this program on itself is
digits = 9 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1, white space = 123, other = 345
The declaration
int ndigit[10];
declares ndigit to be an array of 10 integers. Array subscripts always start at
zero in C, so the elements are ndigit[0], ndigit[1], ..., ndigit[9]. This
is reflected in the for loops that initialize and print the array.
A subscript can be any integer expression, which includes integer variables
like i, and integer constants.
This particular program relies on the properties of the character representation of the digits. For example, the test
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') ...
determines whether the character in c is a digit. If it is, the numeric value of
that digit is
c - '0'
This works only if '0', '1', ... , '9' have consecutive increasing values. Fortunately,
this is true for all character sets.
By definition, chars are just small integers, so char variables and constants
are identical to ints in arithmetic expressions. This is natural and convenient;
for example, c-'0' is an integer expression with a value between 0 and 9
corresponding to the character '0' to '9' stored in c, and is thus a valid subscript
for the array ndigit.
The decision as to whether a character is a digit, white space, or something else is made with the sequence
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
++ndigit[c-'0'];
else if (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\t')
++nwhite;
else
++nother;
The pattern
if (<condition_1>)
<statement_1>
else if (<condition_2>)
<statement_2>
...
...
else
<statement_n>
occurs frequently in programs as a way to express a multi-way decision. The
conditions are evaluated in order from the top until some condition is satisfied;
at that point the corresponding statement part is executed, and the entire construction
is finished. (Any statement can be several statements enclosed in
braces.) If none of the conditions is satisfied, the statement after the final
else is executed if it is present. If the final else and statement are omitted,
as in the word count program, no action takes place. There can be any number
of
else if (<condition>)
<statement>
groups between the initial if and the final else.
As a matter of style, it is advisable to format this construction as we have
shown; if each if were indented past the previous else, a long sequence of
decisions would march off the right side of the page.
The switch statement, to be discussed in Chapter 3, provides another way
to write a multi-way branch that is particularly suitable when the condition is
whether some integer or character expression matches one of a set of constants.
For contrast, we will present a switch version of this program in Section 3.4.
Exercises
1.7 - Functions
In C, a function is equivalent to a subroutine or function in Fortran, or a procedure or function in Pascal. A function provides a convenient way to encapsulate some computation, which can then be used without worrying about its implementation. With properly designed functions, it is possible to ignore how a job is done; knowing what is done is sufficient. C makes the use of functions easy, convenient and efficient; you will often see a short function defined and called only once, just because it clarifies some piece of code.
So far we have used only functions like printf, getchar, and putchar
that have been provided for us; now it's time to write a few of our own. Since C
has no exponentiation operator like the ** of Fortran, let us illustrate the
mechanics of function definition by writing a function power(m, n) to raise an
integer m to a positive integer power n. That is, the value of power(2, 5) is
32. This function is not a practical exponentiation routine, since it handles only
positive powers of small integers, but it's good enough for illustration. (The
standard library contains a function pow(x, y) that computes xy.)
Here is the function power and a main program to exercise it, so you can
see the whole structure at once.
#include <stdio.h>
int power(int m, int n);
/* test power function */
main()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
printf("%d %d %d\n", i, power(2, i), power(-3, i));
return 0;
}
/* power: raise base to n-th power; n >= 0 */
int power(int base, int n)
{
int i, p;
p = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
p = p * base;
return p;
}
A function definition has this form:
<return-type> <function-name>(<parameter declarations, if any>)
{
<declarations>
<statements>
}
Function definitions can appear in any order, and in one source file or several, although no function can be split between files. If the source program appears in several files, you may have to say more to compile and load it than if it all appears in one, but that is an operating system matter, not a language attribute. For the moment, we will assume that both functions are in the same file, so whatever you have learned about running C programs will still work.
The function power is called twice by main, in the line
printf("%d %d %d\n", i, power(2, i), power(-3, i));
Each call passes two arguments to power, which each time returns an integer
to be formatted and printed. In an expression, power(2, i) is an integer just
as 2 and i are. (Not all functions produce an integer value; we will take this
up in Chapter 4.)
The first line of power itself,
int power(int base, int n)
declares the parameter types and names, and the type of the result that the
function returns. The names used by power for its parameters are local to
power, and are not visible to any other function: other routines can use the
same names without conflict. This is also true of the variables i and p: the i in
power is unrelated to the i in main.
We will generally use parameter for a variable named in the parenthesized list in a function definition, and argument for the value used in a call of the function. The terms formal argument and actual argument are sometimes used for the same distinction.
The value that power computes is returned to main by the return statement.
Any expression may follow return:
return <expression>;
A function need not return a value; a return statement with no expression
causes control, but no useful value, to be returned to the caller, as does "falling
off the end" of a function by reaching the terminating right brace. And the calling
function can ignore a value returned by a function.
You may have noticed that there is a return statement at the end of main.
Since main is a function like any other, it may return a value to its caller,
which is in effect the environment in which the program was executed. Typically,
a return value of zero implies normal termination; non-zero values signal
unusual or erroneous termination conditions. In the interests of simplicity, we
have omitted return statements from our main functions up to this point, but
we will include them hereafter, as a reminder that programs should return
status to their environment.
The declaration
int power(int m, int n);
just before main says that power is a function that expects two int arguments
and returns an int. This declaration, which is called a function prototype, has
to agree with the definition and uses of power. It is an error if the definition
of a function or any uses of it do not agree with its prototype.
Parameter names need not agree. Indeed, parameter names are optional in a function prototype, so for the prototype we could have written
int power(int, int);
Well-chosen names are good documentation, however, so we will often use them.
A note of history: The biggest change between ANSI C and earlier versions
is how functions are declared and defined. In the original definition of C, the
power function would have been written like this:
/* power: raise base to n-th power; n >= 0 */
/* (old-style version) */
power(base, n)
int base, n;
{
int i, p;
p = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
p = p * base
return p;
}
The parameters are named between the parentheses, and their types are
declared before the opening left brace; undeclared parameters are taken as int.
(The body of the function is the same as before.)
The declaration of power at the beginning of the program would have
looked like this:
int power();
No parameter list was permitted, so the compiler could not readily check that
power was being called correctly. Indeed, since by default power would have
been assumed to return an int, the entire declaration might well have been
omitted.
The new syntax of function prototypes makes it much easier for a compiler to detect errors in the number of arguments or their types. The old style of declaration and definition still works in ANSI C, at least for a transition period, but we strongly recommend that you use the new form when you have a compiler that supports it.
Exercises
Rewrite the temperature conversion program of Section 1.2 to use a function for conversion. [1]
1.8 - Arguments (Call by Value)
One aspect of C functions may be unfamiliar to programmers who are used
to some other languages, particularly Fortran. In C, all function arguments are
passed "by value." This means that the called function is given the values of its
arguments in temporary variables rather than the originals. This leads to some
different properties than are seen with "call by reference" languages like Fortran
or with var parameters in Pascal, in which the called routine has access to
the original argument, not a local copy.
The main distinction is that in C the called function cannot directly alter a variable in the calling function; it can only alter its private, temporary copy.
Call by value is an asset, however, not a liability. It usually leads to more
compact programs with fewer extraneous variables, because parameters can be
treated as conveniently initialized local variables in the called routine. For
example, here is a version of power that makes use of this property.
/* power: raise base to n-th power; n>=0; version 2 */
int power(int base, int n)
{
int p;
for (p = 1; n > 0; --n)
p = p * base;
return p;
}
The parameter n is used as a temporary variable, and is counted down (a for
loop that runs backwards) until it becomes zero; there is no longer a need for
the variable i. Whatever is done to n inside power has no effect on the argument
that power was originally called with.
When necessary, it is possible to arrange for a function to modify a variable in a calling routine. The caller must provide the address of the variable to be set (technically a pointer to the variable), and the called function must declare the parameter to be a pointer and access the variable indirectly through it. We will cover pointers in Chapter 5.
The story is different for arrays. When the name of an array is used as an argument, the value passed to the function is the location or address of the beginning of the array — there is no copying of array elements. By subscripting this value, the function can access and alter any element of the array. This is the topic of the next section.
1.9 - Character Arrays
The most common type of array in C is the array of characters. To illustrate the use of character arrays and functions to manipulate them, let's write a program that reads a set of text lines and prints the longest. The outline is simple enough:
while (<there's another line>)
if (<it's longer than the previous longest>)
<save it>
<save its length>
<print longest line>
This outline makes it clear that the program divides naturally into pieces. One piece gets a new line, another tests it, another saves it, and the rest controls the process.
Since things divide so nicely, it would be well to write them that way too.
Accordingly, let us first write a separate function getline to fetch the next
line of input. We will try to make the function useful in other contexts. At the
minimum, getline has to return a signal about possible end of file; a more
useful design would be to return the length of the line, or zero if end of file is
encountered. Zero is an acceptable end-of-file return because it is never a valid
line length. Every text line has at least one character; even a line containing
only a newline has length 1.
When we find a line that is longer than the previous longest line, it must be
saved somewhere. This suggests a second function, copy, to copy the new line
to a safe place.
Finally, we need a main program to control getline and copy. Here is
the result.
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXLINE 1000 /* maximum input line size */
int getline(char line[], int maxline);
void copy(char to[], char from[]);
/* print longest input line */
main()
{
int len; /* current line length */
int max; /* maximum length seen so far */
char line[MAXLINE]; /* current input line */
char longest[MAXLINE]; /* longest line saved here */
max = 0;
while ((len = getline(line, MAXLINE)) > 0)
if (len > max) {
max = len;
copy(longest, line);
}
if (max > 0) /* there was a line */
printf("%s", longest);
return 0;
}
/* getline: read a line into s, return length */
int getline(char s[], int lim)
{
int c, i;
for (i = 0; i < lim - 1 && (c = getchar()) != EOF && c != '\n'; i++)
s[i] = c;
if (c == '\n') {
s[i] = c;
++i;
}
s[i] = '\0';
return i;
}
/* copy: copy 'from' into 'to'; assume to is big enough */
void copy(char to[], char from[])
{
int i;
i = 0;
while ((to[i] = from[i]) != '\0')
++i;
}
The functions getline and copy are declared at the beginning of the program,
which we assume is contained in one file.
main and getline communicate through a pair of arguments and a
returned value. In getline, the arguments are declared by the line
int getline(char s[], int lim)
which specifies that the first argument, s, is an array, and the second, lim, is
an integer. The purpose of supplying the size of an array in a declaration is to
set aside storage. The length of the array s is not necessary in getline since
its size is set in main. getline uses return to send a value back to the
caller, just as the function power did. This line also declares that getline
returns an int; since int is the default return type, it could be omitted.
Some functions return a useful value; others, like copy, are used only for
their effect and return no value. The return type of copy is void, which states
explicitly that no value is returned.
getline puts the character '\0' (the null character, whose value is zero)
at the end of the array it is creating, to mark the end of the string of characters.
This convention is also used by the C language: when a string constant like
"hello\n"
appears in a C program, it is stored as an array of characters containing the
characters of the string and terminated with a '\0' to mark the end.
The %s format specification in printf expects the corresponding argument to
be a string represented in this form. copy also relies on the fact that its input
argument is terminated by '\0', and it copies this character into the output
argument. (All of this implies that '\0' is not a part of normal text.)
It is worth mentioning in passing that even a program as small as this one
presents some sticky design problems. For example, what should main do if it
encounters a line which is bigger than its limit? getline works safely, in that
it stops collecting when the array is full, even if no newline has been seen. By
testing the length and the last character returned, main can determine whether
the line was too long, and then cope as it wishes. In the interests of brevity, we
have ignored the issue.
There is no way for a user of getline to know in advance how long an
input line might be, so getline checks for overflow. On the other hand, the
user of copy already knows (or can find out) how big the strings are, so we
have chosen not to add error checking to it.
Exercises
Revise the main routine of the longest-line program so it will correctly print the length of arbitrarily long input lines, and as much as possible of the text. [1]
Write a program to print all input lines that are longer than 80 characters. [1]
Write a program to remove trailing blanks and tabs from each line of input, and to delete entirely blank lines. [1]
Write a function
reverse(s)that reverses the character strings. Use it to write a program that reverses its input a line at a time. [1]
1.10 - External Variables and Scope
The variables in main, such as line, longest, etc., are private or local to
main. Because they are declared within main, no other function can have
direct access to them. The same is true of the variables in other functions; for
example, the variable i in getline is unrelated to the i in copy. Each local
variable in a function comes into existence only when the function is called, and
disappears when the function is exited. This is why such variables are usually
known as automatic variables, following terminology in other languages. We
will use the term automatic henceforth to refer to these local variables.
(Chapter 4 discusses the static storage class, in which local variables do
retain their values between calls.)
Because automatic variables come and go with function invocation, they do not retain their values from one call to the next, and must be explicitly set upon each entry. If they are not set, they will contain garbage.
As an alternative to automatic variables, it is possible to define variables that are external to all functions, that is, variables that can be accessed by name by any function. (This mechanism is rather like Fortran COMMON or Pascal variables declared in the outermost block.) Because external variables are globally accessible, they can be used instead of argument lists to communicate data between functions. Furthermore, because external variables remain in existence permanently, rather than appearing and disappearing as functions are called and exited, they retain their values even after the functions that set them have returned.
An external variable must be defined, exactly once, outside of any function;
this sets aside storage for it. The variable must also be declared in each function
that wants to access it; this states the type of the variable. The declaration
may be an explicit extern statement or may be implicit from context. To
make the discussion concrete, let us rewrite the longest-line program with line,
longest, and max as external variables. This requires changing the calls,
declarations, and bodies of all three functions.
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXLINE 1000 /* maximum input line size */
int max; /* maximum length seen so far */
char line[MAXLINE]; /* current input line */
char longest[MAXLINE]; /* longest line saved here */
int getline(void);
void copy(void);
/* print longest input line; specialized version */
main()
{
int len;
extern int max;
extern char longest[];
max = 0;
while ((len = getline()) > 0)
if (len > max) {
max = len;
copy();
}
if (max > 0) /* there was a line */
printf("%s", longest);
return 0;
}
/* getline: specialized version */
int getline(void)
{
int c, i;
extern char line[];
for (i = 0; i < MAXLINE - 1
&& (c = getchar()) != EOF && c != '\n'; ++i)
line[i] = c;
if (c == '\n') {
line[i] = c;
++i;
}
line[i] = '\0';
return i;
}
/* copy: specialized version */
void copy(void)
{
int i;
extern char line[], longest[];
i = 0;
while ((longest[i] = line[i]) != '\0')
++i;
}
The external variables in main, getline, and copy are defined by the
first lines of the example above, which state their type and cause storage to be
allocated for them. Syntactically, external definitions are just like definitions of
local variables, but since they occur outside of functions, the variables are external.
Before a function can use an external variable, the name of the variable
must be made known to the function. One way to do this is to write an
extern declaration in the function; the declaration is the same as before except
for the added keyword extern.
In certain circumstances, the extern declaration can be omitted. If the
definition of an external variable occurs in the source file before its use in a particular
function, then there is no need for an extern declaration in the function.
The extern declarations in main, getline and copy are thus redundant.
In fact, common practice is to place definitions of all external variables at
the beginning of the source file, and then omit all extern declarations.
If the program is in several source files, and a variable is defined in file1
and used in file2 and file3, then extern declarations are needed in file2 and
file3 to connect the occurrences of the variable. The usual practice is to collect
extern declarations of variables and functions in a separate file, historically
called a header, that is included by #include at the front of each source file.
The suffix .h is conventional for header names. The functions of the standard
library, for example, are declared in headers like <stdio.h>. This topic is
discussed at length in Chapter 4, and the library itself in Chapter 7 and Appendix B.
Since the specialized versions of getline and copy have no arguments,
logic would suggest that their prototypes at the beginning of the file should be
getline() and copy(). But for compatibility with older C programs the
standard takes an empty list as an old-style declaration, and turns off all argument
list checking; the word void must be used for an explicitly empty list.
We will discuss this further in Chapter 4.
You should note that we are using the words definition and declaration carefully when we refer to external variables in this section. "Definition" refers to the place where the variable is created or assigned storage; "declaration" refers to places where the nature of the variable is stated but no storage is allocated.
By the way, there is a tendency to make everything in sight an extern variable
because it appears to simplify communications — argument lists are short
and variables are always there when you want them. But external variables are
always there even when you don't want them. Relying too heavily on external
variables is fraught with peril since it leads to programs whose data connections
are not at all obvious — variables can be changed in unexpected and even inadvertent
ways, and the program is hard to modify. The second version of the
longest-line program is inferior to the first, partly for these reasons, and partly
because it destroys the generality of two useful functions by wiring into them
the names of the variables they manipulate.
At this point we have covered what might be called the conventional core of C. With this handful of building blocks, it's possible to write useful programs of considerable size, and it would probably be a good idea if you paused long enough to do so. These exercises suggest programs of somewhat greater complexity than the ones earlier in this chapter.
Exercises
Write a program
detabthat replaces tabs in the input with the proper number of blanks to space to the next tab stop. Assume a fixed set of tab stops, say every columns. Should be a variable or a symbolic parameter? [1]Write a program
entabthat replaces strings of blanks by the minimum number of tabs and blanks to achieve the same spacing. Use the same tab stops as fordetab. When either a tab or a single blank would suffice to reach a tab stop, which should be given preference? [1]Write a program to "fold" long input lines into two or more shorter lines after the last non-blank character that occurs before the th column of input. Make sure your program does something intelligent with very long lines, and if there are no blanks or tabs before the specified column. [1]
Write a program to remove all comments from a C program. Don't forget to handle quoted strings and character constants properly. C comments do not nest. [1]
Write a program to check a C program for rudimentary syntax errors like unbalanced parentheses, brackets and braces. Don't forget about quotes, both single and double, escape sequences, and comments. (This program is hard if you do it in full generality.) [1]
Questions
Machine-dependent object sizes
- Question
- Answer
The range of both
intandfloatdepends on the machine you are using [...]. [...] The sizes of these objects [i.e.,char,short,long,double] are also machine-dependent.
What are the practical consequences of this, if any?
TBD
Type coercion of symbolic constants
- Question
- Answer
Something like
#define UPPER 300
defines the UPPER symbolic constant as 300. But what is 300 and how is it treated in different contexts (e.g., comparison with other integers, floats, strings, etc.)?
TBD
Function prototypes
- Question
- Answer
The following example of the power function is given earlier in this chapter:
#include <stdio.h>
int power(int m, int n);
/* test power function */
main()
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
printf("%d %d %d\n", i, power(2, i), power(-3, i));
return 0;
}
/* power: raise base to n-th power; n >= 0 */
int power(int base, int n)
{
int i, p;
p = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
p = p * base;
return p;
}
The highlighted declaration above is the function prototype for power — what is the importance of this? It seems like a function definition itself should be enough. Is it important for function prototypes to appear before main?
It is an error if the definition of a function or any uses of it do not agree with its prototype.
Why does a function's prototype need to be declared in addition to its definition?
TBD
Quick takeaways
- Comments: Comments may appear anywhere a blank or tab or newline can.
whileloop syntax: The body of awhilecan be one or more statements enclosed in braces, as in the temperature converter, or a single statement without braces.- Truncated integer division: In C, as in many other languages, integer division truncates: any fractional part is discarded.
printfarguments and types: Each%construction in the first argument ofprintfis paired with the corresponding second argument, third argument, etc.; they must match up properly by number and type, or you'll get wrong answers.- Use of expressions for values: In any context where it is permissible to use the value of a variable of some type, you can use a more complicated expression of that type.
forloop syntax: As with thewhile, the body of the loop can be a single statement, or a group of statements enclosed in braces. The initialization, condition, and increment can be any expressions.- Text streams: Text input or output, regardless of where it originates or where it goes to, is dealt with as streams of characters. A text stream is a sequence of characters divided into lines; each line consists of zero or more characters followed by a newline character.
- Using assignments as values: In C, any assignment, such as
c = getchar(), is an expression and has a value, which is the value of the left hand side after the assignment. This means that an assignment can appear as part of a larger expression. If you use this pattern to make comparisons, then make sure you wrap the assignment in parentheses; for example, write(c = getchar()) != EOFinstead ofc = getchar() != EOF. The reason is that!=has higher precedence than=, which meansc = getchar() != EOFwould be equivalent to writingc = (getchar() != EOF). In general, wrapping assignments in parentheses makes it unambiguous what you are trying to do. printfsyntax for floats and doubles:printfuses%ffor bothfloatanddouble- Null statements in loops: The grammatical rules of C require that a
forstatement have a body. An isolated semicolon, called a null statement, is there to satisfy that requirement. You will often see it on a separate line for the sake of visibility. - Assignments have values (multiple assignments on one line): The line
nl = nw = nc = 0;sets all three variables to zero. This is not a special case, but a consequence of the fact that an assignment is an expression with a value and assignments associate from right to left. It's as if we had writtennl = (nw = (nc = 0));. - External variables: Syntactically, external definitions are just like definitions of local variables, but since they occur outside of functions, the variables are external. Before a function can use an external variable, the name of the variable must be made known to the function. One way to do this is to write an
externdeclaration in the function; the declaration is the same as before except for the added keywordextern.